
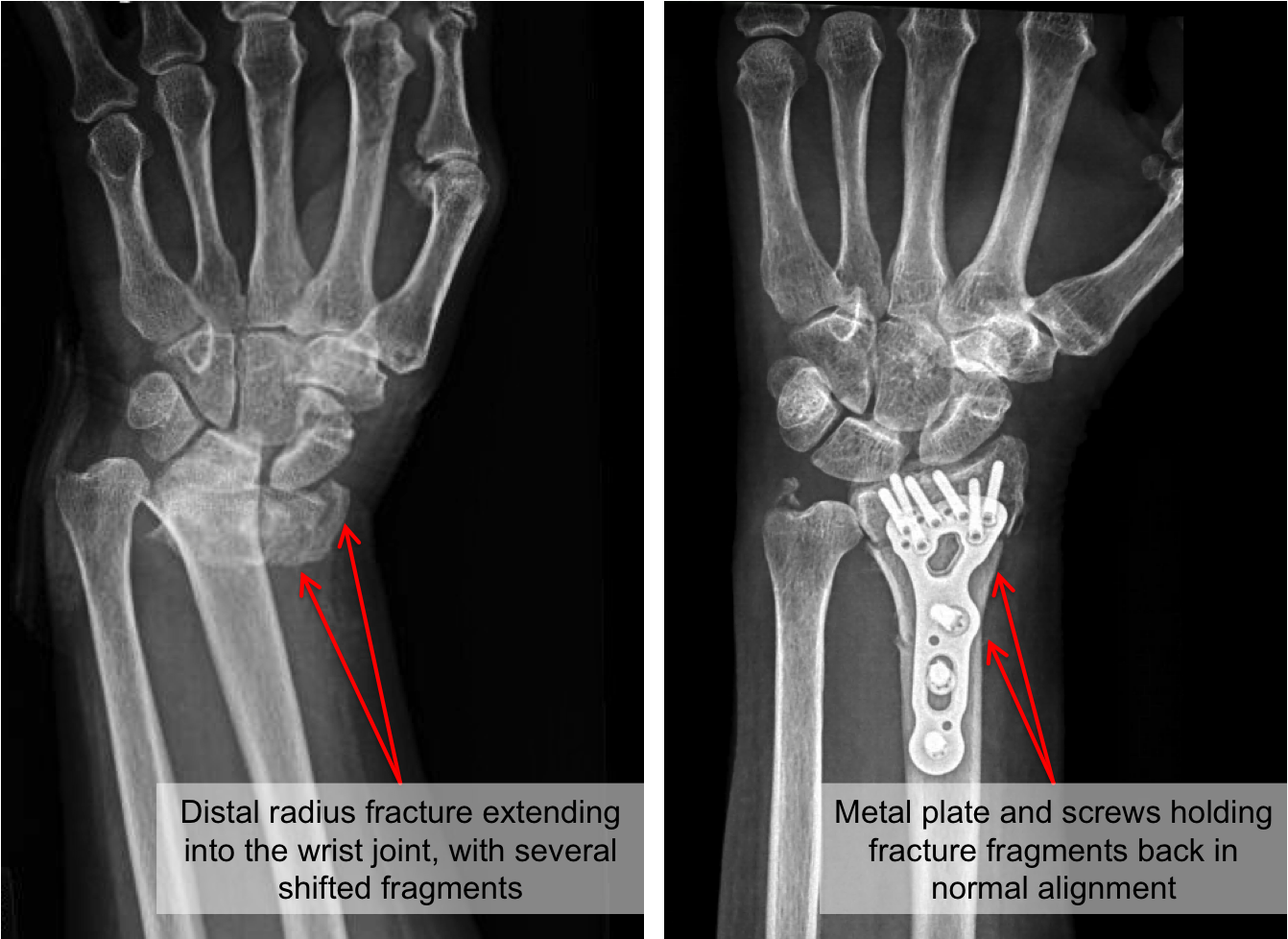
Different surgical methods are available, all with their inherent advantages and disadvantages. In Sweden, 20–30% of radius fractures are treated surgically. Unstable fractures tend to heal in a non-favorable anatomical position, and surgical treatment is usually recommended. Benign non-displaced fractures are commonly treated non-operatively in a plaster cast. For those interested in accessing the data, please send requests to Per Tornvall, Professor, Head of Department of Clinical Science and Education, Sodersjukhuset, Karolinska Institute, email: The authors received no specific funding for this work.Ĭompeting interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.įor a distal radial fracture, the most common of all fractures, there is no consensus regarding optimal treatment. The authors are not allowed to upload the file with data from the Swedish National Patient Registry, according to the ethical approval. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.ĭata Availability: Data are available from the Karolinska Institute Data Access for researchers who meet the criteria for access to confidential data.
Received: Accepted: NovemPublished: November 16, 2018Ĭopyright: © 2018 Saving et al.

PLoS ONE 13(11):Įditor: Robert Daniel Blank, Medical College of Wisconsin, UNITED STATES Citation: Saving J, Ponzer S, Enocson A, Mellstrand Navarro C (2018) Distal radius fractures-Regional variation in treatment regimens.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
